
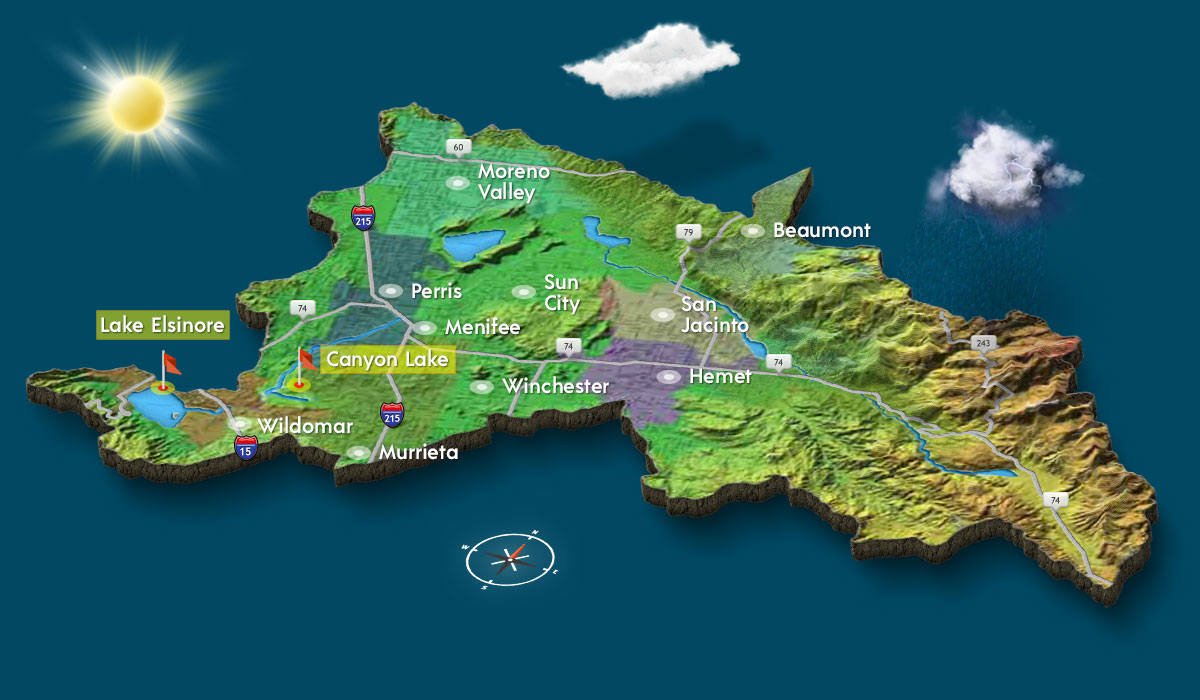
Lake Elsinore and Canyon Lake are part of the San Jacinto River Watershed. The Watershed covers 780 square miles in the western half of Riverside County. It begins in the San Jacinto Mountains and runs west through Canyon Lake, ending in Lake Elsinore.
Lake Elsinore Watershed
Lake Elsinore is the largest natural freshwater lake in Southern California. With its own 45 sq mi watershed, it is located at the lowest point within the San Jacinto River watershed of 780 sq mi at the end of the San Jacinto River.
San Jacinto River Watershed
The San Jacinto River is a 42-mile-long river in Riverside County, California. The river’s headwaters are in Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument. Water flows downstream and eventually ends in Lake Elsinore.
The natural flow of water through the San Jacinto Watershed carries nutrient-rich sediment into our lakes each year. The sediment carries with it high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus that hurt water quality and threaten aquatic life in Canyon Lake and Lake Elsinore.
Tributaries of the San Jacinto River include:
- Cottonwood Canyon Creek
- Canyon Lake
- Salt Creek
- Perris Valley Channel
- Bautista Creek
- Indian Creek
- North Fork San Jacinto River
- Logan Creek
- Stone Creek
- Black Mountain Creek
- Fuller Mill Creek
- South Fork San Jacinto River
- Dry Creek
- Strawberry Creek
- Coldwater Creek
- Spillway Canyon Creek
- Lake Hemet
- Herkey Creek
- Fobes Canyon Creek
- Pipe Creek
- Martinez Creek
- Gold Shot Creek
- Penrod Canyon Creek
What is a Watershed?
A Watershed is an area of land that drains into a lake or river. As rainwater and melting snow run downhill, they carry sediment and other materials into our streams, lakes and groundwater.
Watersheds provide water for drinking, irrigation and streams. Many people also enjoy the lakes and streams for their beauty, boating, fishing and swimming. Healthy watersheds also provide food and shelter for wildlife.
Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Board
The Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board is one of nine regional Boards overseen by the State Water Resources Control Board. The mission of the State Water Board is to ensure the highest reasonable quality for waters of the State, while allocating those waters to achieve the optimum balance of beneficial uses. Individual Regional Boards develop and enforce water quality objectives and implementation plans that will best protect the beneficial uses of the State’s waters.
- The Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Board first listed Lake Elsinore as impaired in 1994 due to its history of periodic fish kills and excessive algae blooms.
- Canyon Lake was added in 1998 based on its periodic algal blooms and fish kills, neither as significant as those that occur in Lake Elsinore.
- The Santa Ana Regional Board has been a cooperative partner with LESJWA and is a member agency of the Lake Elsinore/Canyon Lake TMDL Task Force
The Lakes at a Glance
Canyon Lake

Canyon Lake is a reservoir located inside a private-gated, master-planned community in Southern California. This recreational, 338- acre lake sits near the end of the San Jacinto River where incoming water is captured and stored. Blocked by the Railroad Canyon Reservoir Dam, this lake often spills over into Lake Elsinore during heavy storm events.
Lake Elsinore

As Southern California’s largest natural fresh water, Lake Elsinore is Southern California’s premier destination for water recreation, extreme sports, sky-diving and shopping. At just about an hour from Los Angeles, Orange and San Diego Counties, Lake Elsinore is a beautiful weekend destination for Southern California families to recreate.
